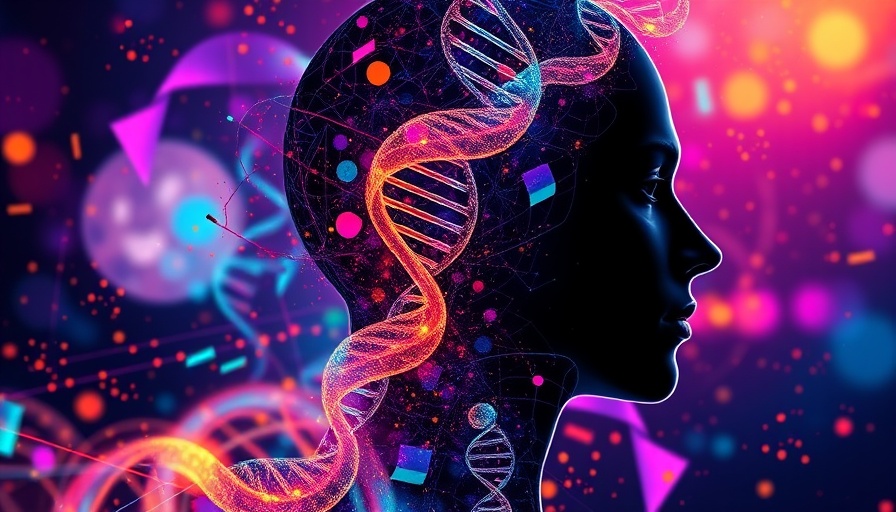

A Revolutionary Leap in Genetic Editing
In a groundbreaking era for biotechnology, the next-generation Crispr technology is shining a light on the path to correcting genetic 'spelling errors'. These advancements in genetic editing are becoming a beacon of hope for those battling rare diseases that, until recently, seemed untreatable. This innovative approach shifts from the destructive edits of first-generation Crispr to a precise 'find and replace' method, providing a new avenue for treating conditions where misspellings occur in the genome.
Breaking Barriers in Genetic Therapy
Treatments previously constrained by technological limitations are now evolving. The key challenge with previous gene-editing techniques was the requirement for excising parts of the genetic code, which wasn’t suitable for conditions needing precision alterations. For diseases like progeria, where a single base pair error can have lifelong consequences, the need was for a subtle correction rather than a blunt deletion.
Future Predictions and Trends
As we move forward, the field is set to undergo transformative changes. Emerging delivery systems, such as adeno-associated virus vectors, and advancements in in vivo editing are expected to revolutionize how we approach genetic disorders. These innovations promise to expand the reach and efficacy of gene therapy, opening doors to treat a broader array of conditions directly within crucial organs and tissues. The ongoing development of nonviral systems like lipid nanoparticles suggests a future where treatments are not only more effective but also safer and more affordable.
Relevance to Current Events
This innovation arrives at a critical time as the global healthcare landscape seeks more efficient solutions to combat rare diseases. The recent FDA approval of Crispr therapy for sickle cell disease sets a promising precedent and highlights the real-world impact of these scientific breakthroughs. The potential for Crispr to alter the course of genetic diseases holds significant implications for healthcare, offering a potential paradigm shift in how we tackle chronic and hereditary conditions.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment