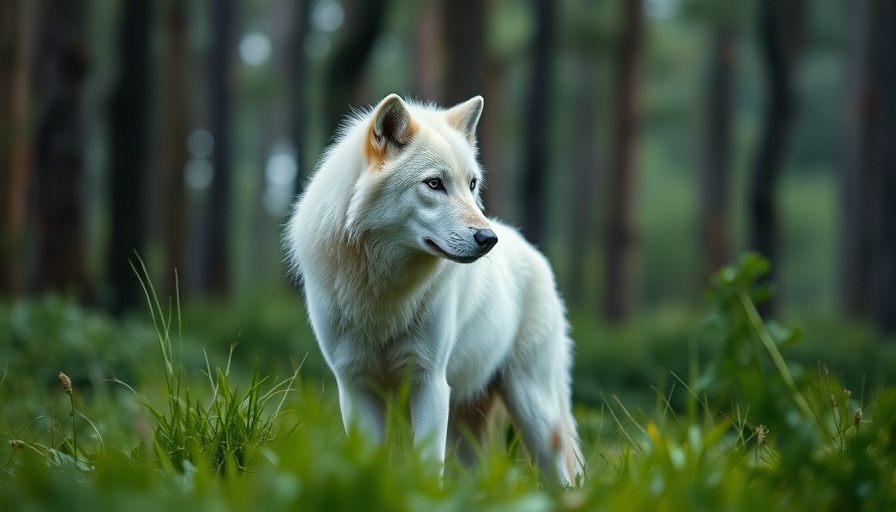

Exploring the Ethics and Implications of Colossal’s 'De-Extinction' Efforts
In the vast expanses of the northern U.S., a fascination with epic narratives and mythical creatures fuels an ongoing debate. Hidden within a strictly monitored 2,000-acre preserve are three strikingly snow-white animals that a Texas-based startup, Colossal Biosciences, claims to have revived from extinction. Dubbed as dire wolves, an ancient canine species that vanished 13,000 years ago, these creatures raise pressing questions about the ethics of genetic engineering and the future of biotechnology in conservation.
What Does 'De-Extinction' Really Mean?
Colossal's claim of bringing back a long-extinct species draws both intrigue and skepticism. Using cutting-edge gene editing techniques, Colossal extracted DNA from dire wolf remains and combined it with gray wolf cells. Critics, however, are challenging the authenticity of these creations. As Anders Bergström, a canine evolution expert points out, the modifications made—20 genetic alterations—are insufficient for claiming these animals truly represent the dire wolf lineage. Instead, they may resemble a unique genetically-modified version of a gray wolf.
Are We Playing God? The Ethical Debate
This undertaking to resurrect species poses ethical dilemmas central to discussions on biotechnological advancements. Is it right to play god in the name of conservation? Critics of Colossal worry that such ventures could divert attention and resources away from crucial conservation work aimed at existing species on the brink of extinction. The debate transcends mere science; it invites society to reflect on our role in shaping the destinies of living beings.
Public Perception: Allure vs. Skepticism
The spectacle of ‘de-extinction’ captivates public imagination, checked by a wave of skepticism from the scientific community. Critics observe that while the allure of bringing back charismatic megafauna can increase public interest in conservation, it may also lead to a false sense of security regarding biodiversity. The reality is that genetic tinkering cannot substitute for the complex ecosystems and conservation measures necessary for surviving species.
Future Trends in Biotechnology and Conservation
The controversy surrounding Colossal’s wolves is just one chapter in the evolving tale of biotechnology's role in conservation. As technology progresses, debates on genetic modification will persist, highlighting a potential shift in understanding our responsibility towards nature. A move towards responsible innovation that prioritizes ecological balance and biodiversity may define future advancements.
Practical Applications of Biotechnology in Conservation
Despite the controversies, there are practical applications of biotech in conservation that can yield real benefits. From genomic sequencing that identifies genetic diversity in endangered species to biobanking as a means of preserving genetic material, the potential for biotechnology to support biodiversity is immense when applied ethically. Using science responsibly could become the foundation for sustainable management practices in wildlife conservation.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Biotechnology and Conservation
As we traverse through these complex discussions about biotechnology and species revival, including Colossal's enchanting yet contentious claims, we must remember the broader implications of these actions. The call for a conscientious approach to technology in conservation is more pressing than ever, as it shapes our relationship with the living world. Embracing innovation wisely could lead to a brighter future for both biodiversity and life on Earth.
Now is the time to engage deeply in these conversations about biotechnology's role in conservation. Let’s participate in shaping a responsible path for the future and make informed decisions that resonate across the scientific, ethical, and public spheres.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment