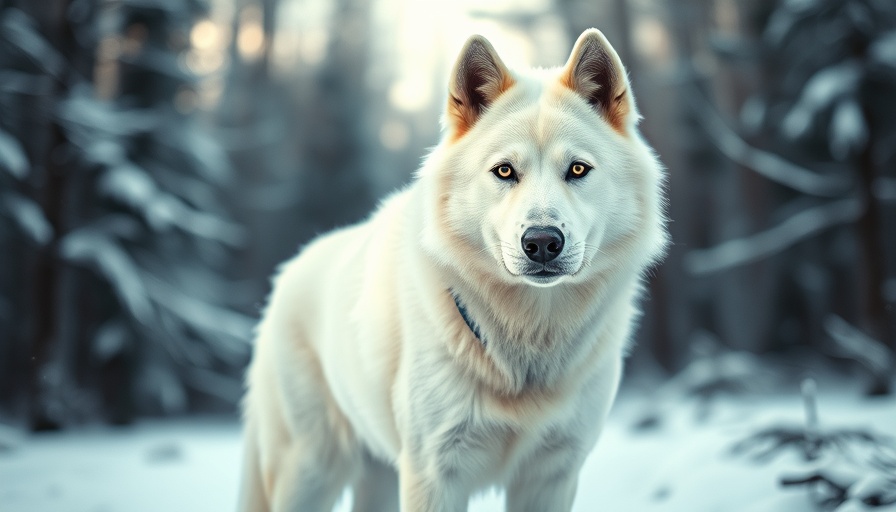

Reviving Extinct Species: The Groundbreaking Case of the Dire Wolf
In a thrilling blend of advanced biotechnology and wildlife conservation, Colossal Biosciences has announced its success in editing the DNA of modern gray wolves to produce what it claims is a de-extinct species: the dire wolf. These enigmatic creatures, which roamed North America over 10,000 years ago, are being brought back into the realm of possibility, prompting questions about the boundaries of science and the ethical implications of de-extinction.
What Makes a True Dire Wolf?
The dire wolves at the center of this claim bear significant physical traits purportedly reminiscent of their ancient counterparts. Ben Lamm, CEO of Colossal, indicates these wolves demonstrate pronounced shoulders, a wider head, and more robust haunches than today’s gray wolves. Each pup tips the scales at around 80 pounds at just five months old, indicating a future size surpassing their modern relatives. Notably, they also sport white fur, reminiscent of the iconic dire wolves from the popular series, “Game of Thrones.”
The Science Behind De-extinction
Colossal's approach to de-extinction diverges from traditional cloning methodologies. Instead of using preserved DNA, the company seeks to identify and engineer genes from extinct species into the genomes of their nearest living relatives. This technique not only allows scientists to bring back visual aspects of the dire wolf but also prompts discourse about how we define a species’ identity. Are these wolves truly dire wolves, or merely a genetically modified version of them?
Implications for Biodiversity and Ecology
The implications of de-extinction extend far beyond just reviving iconic species. As the climate crisis prompts discussions about biodiversity loss, the resurrection of these species could serve as a case study for future conservation efforts. If successful, the techniques developed by Colossal could enable restoration of ecosystems previously disrupted by extinction, bringing back balance to our planet’s threatened habitats. However, this raises ethical concerns: what are the consequences of introducing a genetically altered species into modern ecosystems?
The Commercial Aspects of De-extinction
With a valuation exceeding $10 billion and substantial investment, Colossal Biosciences illustrates the fervor surrounding biotechnological innovation. Investors are keen on funding ventures that promise both scientific breakthroughs and potential returns on investment. As they aim to bring back not only the dire wolf but also other famous extinct species, the intersection of science and capitalism showcases where future growth could lie.
What Does This Mean for Industry and Innovation?
For executives across industries, the emergence of biotechnology companies like Colossal outlines trends in consumer expectations and ethical considerations regarding science. With ongoing discussions surrounding AI integration in corporate strategies, the developments in biotechnology also highlight the necessity for proactive approaches, ensuring that these technologies align with public sentiment and ethical guidelines.
Conclusion: Engaging with Tomorrow’s Ethical Landscape
The notion of resurrecting a legendary creature like the dire wolf invites us to re-think our relationship with nature and technology. As business leaders explore innovative pathways for growth through technologies like AI and biotechnology, they must also grapple with the complex ethical questions that emerge alongside scientific advancements. The potential benefits are immense, but they come with responsibilities that must not be overlooked. Engaging with these critical conversations today is essential for shaping a sustainable and ethical future in business and conservation.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment